# this is a Julia chunk
1 + 23| Resource | Information |
|---|---|
| Git + DOI | Git 10.5281/zenodo.17589694 |
| Short Description | This notebook demonstrates the integration of the programming language Julia in quarto .qmd files. We also briefly showcase the open-source symbolic computer algebra Julia package Oscar. |
Julia is a fast, dynamic and modern programming language which is often used in scientific computing (Bezanson et al. (2017)). Follow the Julia Website to install its latest version. There is a detailed page on quarto.org on using Julia in .qmd files. It is recommended to set engine: julia in the header which works with the Julia version manager juliaup. When quarto detects a non-R chunk in .qmd, it automatically selects a Jupyter engine. When aiming to present Julia Code, the Julia engine provides more flexibility. Specifying {julia} in the chunk head, triggers the Julia execution.
# this is a Julia chunk
1 + 23To call multiple languages in a single .qmd file with a julia engine, one has to specify the appropriate R and / or Python wrappers. When solely using R and Python code, don’t specify an engine, as then Jupyter is selected (see quarto details).
# this is a Julia chunk
using Pkg
Pkg.add("RCall")
Pkg.add("PythonCall")
using RCall
using PythonCall# this is an R chunk
1 * pi# this is an R chunk
1 * pi3.141592653589793# this is a Python chunk
import math
math.sqrt(16)# this is a Python chunk
import math
math.sqrt(16)Python: 4.0To use Julia packages in .qmd code chunks, install them with Using Pkg and Pkg.add("package"), and load. We briefly showcase the open-source symbolic computer algebra Julia package Oscar, which is especially relevant for mathematicians (“OSCAR – Open Source Computer Algebra Research System, Version 1.5.0” (2025), Decker et al. (2025)). In particular, it supports the identification of statistical models and estimators.
Pkg.add("Graphviz_jll")
Pkg.add("Oscar")
using Graphviz_jll
using Oscar# this is a julia chunk
Qx, x = polynomial_ring(QQ, [:x1,:x2])
R = grade(Qx, [1,2])[1]
f = R(x[1]^2+x[2])
println("The degree of the function f is ", degree(f), ".")The degree of the function f is [2].Oscar is actively developed and publicly funded. For more information, visit their website. Finally, we show how the graph of the 3-simplex can be created and plotted with Oscar.
G = vertex_edge_graph(simplex(5))
visualize(G; backend=:graphviz, filename="files/julia_graph.dot")
run(`dot -Tpng -Gdpi=600 files/julia_graph.dot -o files/graph.png`)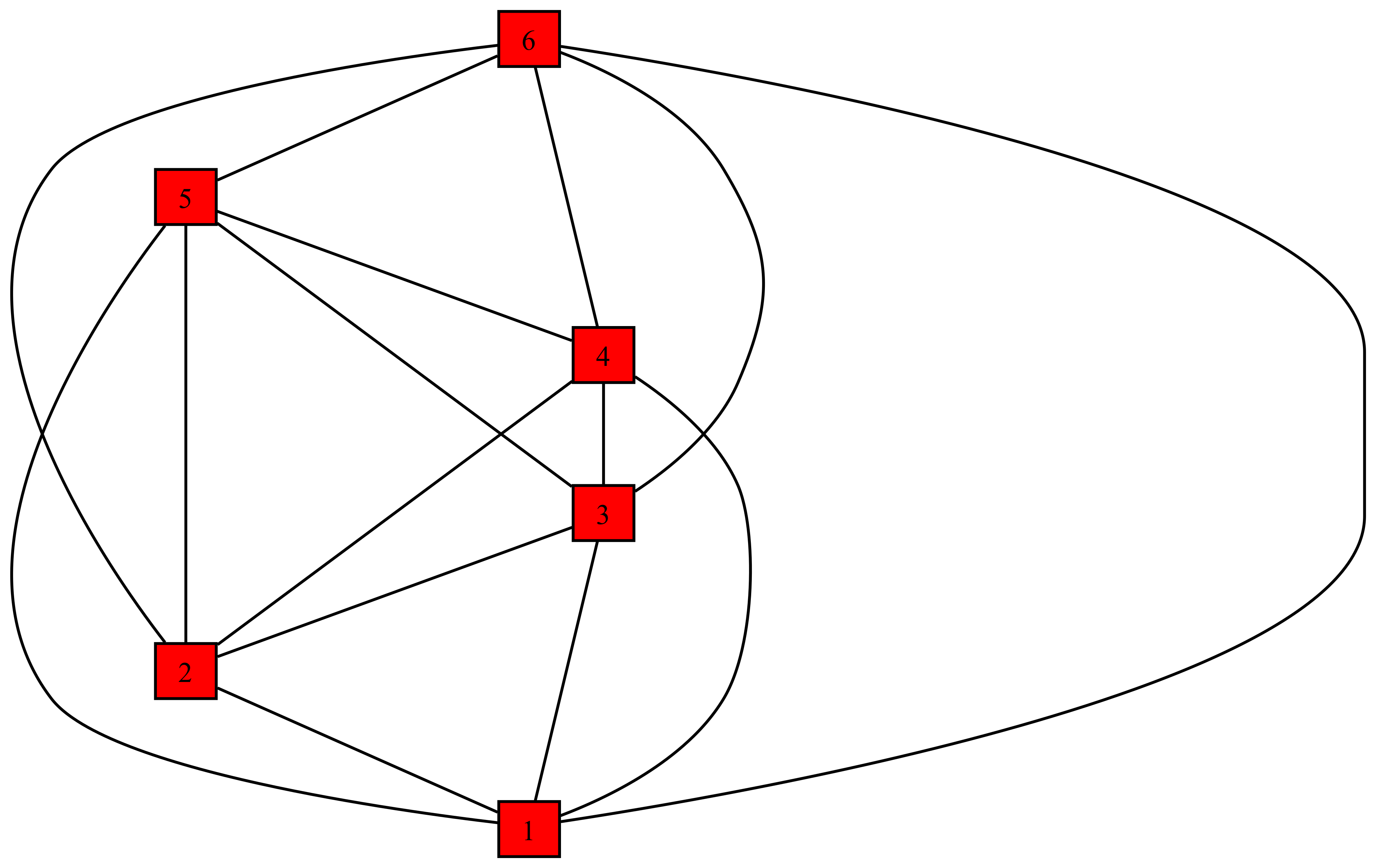
Please cite our community with the following bib item.
@article{Mareis_Haug_Drton_2025,
title={MaRDI's Zenodo Community for Graphical Modeling and Causal Inference},
volume={2},
journal={Proceedings of the Conference on Research Data Infrastructure},
author={Mareis, Leopold and Haug, Stephan and Drton, Mathias},
year={2025},
month={Sep.}
}License Information: Please follow the above DOI for license information of data and code.
Contact: If you have suggestions, feel free to create an issue or contact the community moderators (mardi’at’statistics.cit.tum.de).